
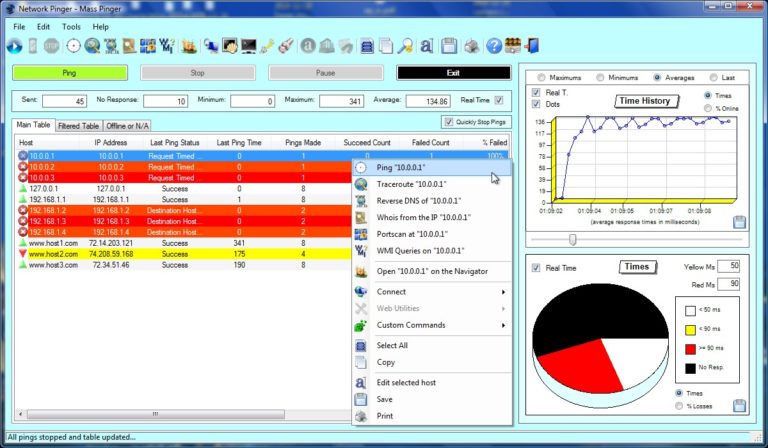
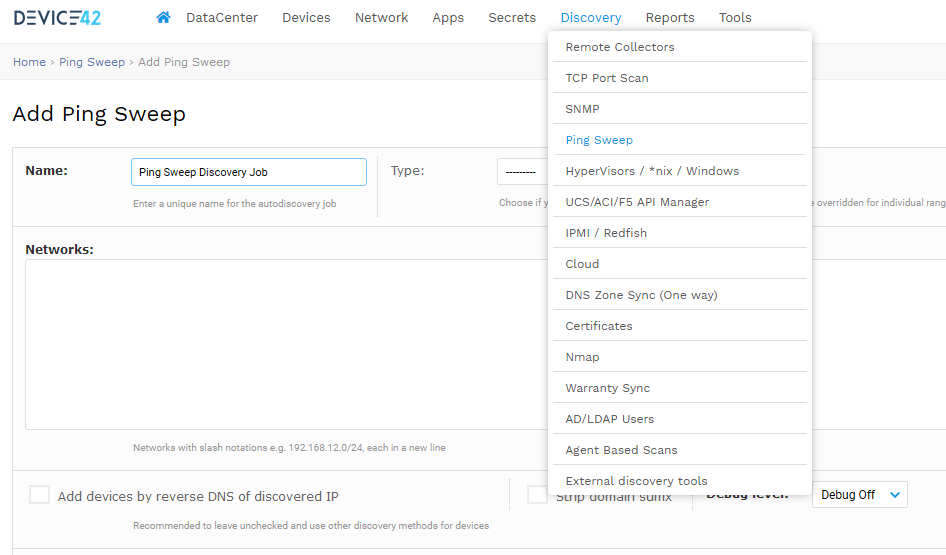
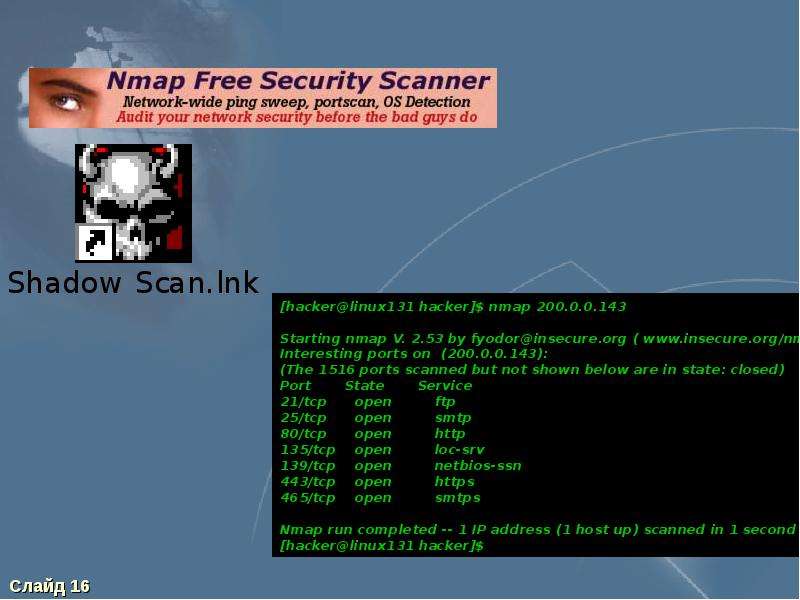
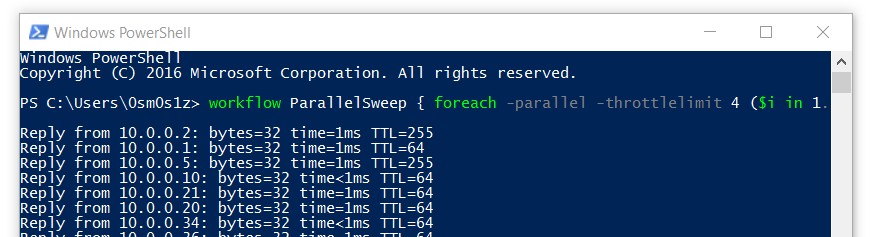
Such an attack can be used to gather information about a network before launching more sophisticated attacks. If a target host responds to the ping, its IP address is revealed to the attacker. By sending ICMP echo requests (pings) to multiple destination addresses, the attacker can determine which IP addresses are associated with active Internet Protocol (IP) endpoints. Using Ping Sweeps for Attack PurposesĪn attacker can use ping sweeps to identify active hosts on a network. Nmap can be used to perform a ping sweep of an entire subnet in order to quickly identify live hosts before performing more detailed scans. If an active host responds to the request, it indicates that the host is alive and reachable on the network. It works by sending ICMP Echo Request packets, commonly known as “pings”, to each IP address in the specified range.
#Ping sweep windows#
That aid in the administration of local and remote systems named PsPing is part of a growing kit of Sysinternals command-line tools Simply add -u to have PsPing perform a UDPīandwidth test. Note that the test must run for at least one second after warmup for a IP address for 10 seconds and produces a histogram with 100 buckets. This command tests bandwidth to a PsPing server listening at the target Server, printing a histogram with 100 buckets when completed: psping -l 8k -n 10000 -h 100 192.168.2.2:5000 Measures the round trip latency of sending an 8KB packet to the target The -s option and the source address and port the server will bind to: psping -s 192.168.2.2:5000Ī buffer size is required to perform a TCP latency test. To configure a server for latency and bandwidth tests, simply specify Possible, only printing a summary when finished with the 100 iterationsĪnd 1 warmup iteration: psping -n 100 -i 0 -q marklap:80 The followingĬommand executes connect attempts against the target as quickly as To execute a TCP connect test, specify the port number. This command executes an ICMP ping test for 10 iterations with 3 warmup Warmup for the specified iterations (default is 2x CPU cores). Number of outstanding I/Os (default is min of 16 and 2x CPU cores). The server can serve both latency and bandwidth tests and remains activeĬlient: psping |] ] ] Warmup with the specified number of iterations (default is 5). Receive from the server instead of sending. Open source firewall port during the run.
TCP ping usage: psping |] ] Ĭlient: psping |] ] ] Warmup with the specified number of iterations (default is 1).įor high-speed ping tests use -q and -i 0. Ping until stopped with Ctrl+C and type Ctrl+Break for statistics. Number of pings or append 's' to specify seconds e.g. Append 'k' for kilobytes and 'm' for megabytes. Specify a comma-separated list of times to create a custom histogram (e.g. If you specify a single argument, it's interpreted as a bucket count and the histogram will contain that number of buckets covering the entire time range of values. Print histogram (default bucket count is 20). Use the following command-line options to show the usageĬopy PsPing onto your executable path. PsPing implements Ping functionality, TCP ping, latency and bandwidth


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
